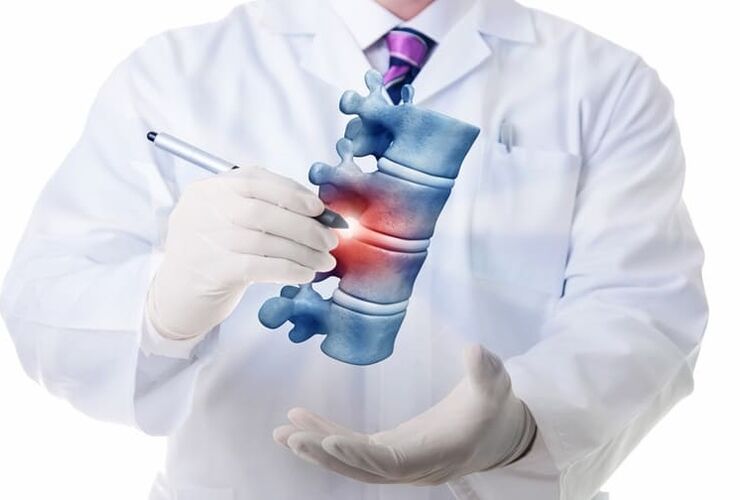
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine does not present as often as osteochondrosis in other departments, but it is as young as other types of this disease. To date, it has been diagnosed in 20-year-olds, and it is related to lifestyle and diet.
Thoracic vertebral osteochondrosis is the least common pathological form, but the most dangerous of all types of osteochondrosis. Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are very atypical and can be attributed to other conditions, such as myocardial infarction or angina.
The disease does pose a threat because over time, without proper treatment, osteochondrosis can lead to cardiac dysfunction, and the lines between these diseases are very thin.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Due to its anatomical features, the thoracic spine is less mobile. Because of this, it is less loaded, so osteochondrosis occurs much less frequently here. When the first lesions appear in the chest, the patient does not feel any signs of the disease for a long time due to the slow progression of the disease.
The symptoms of osteochondrosis depend on the stage of development of the disease and are completely related to it. In the early stages, symptoms are less pronounced, whereas advanced osteochondrosis can cause severe symptoms such as heart pain and increased heart rate. The disease manifests as follows:
- In the first stage of disease development, the discomfort of osteochondrosis occurs due to the destruction of the integrity of the intervertebral disc. Vigorous clumsy movements or heavy loads in the thoracic region may cause the rupture. During these moments, patients experience increased sensitivity in this area of the spine and experience severe pain and muscle tension. The patient notes that the sensation is similar to an electrical discharge through the back;
- Secondary disease is characterized by a herniated disc that protrudes up to 5 mm. The spine becomes unstable, the diagnosis requires a thorough analysis of the patient's health, as the patient constantly complains of discomfort and pain behind the chest, muscle tension, which may be symptoms of various pathologies;
- Third-degree thoracic vertebral osteochondrosis has a more pronounced presentation - pain becomes more frequent, patients have breathing problems (sudden shortness of breath, feeling a lack of air), feel headaches, and have heart interruptions with osteochondrosis.
important!For patients, the fourth stage of the disease is the most dangerous. Here, osteophytes appear on the surface of the vertebrae, compressing the spinal cord and nerve endings.
At different stages of the disease, patients suffer from the following pathological symptoms:
- Intercostal neuralgia - a feeling of severe pain in the breastbone. At first, the pain may appear in only one place, but after a while, the pain completely covers the person's chest. The patient has difficulty breathing and changes in body position. If you try to bend over, move, or stand up from one place, the painful sensation increases significantly;
- Muscle spasms - The pain in the back muscles is so intense that the pain spreads to the lower back and can even radiate to the abdomen and shoulders. Spasticity is reflex in nature, i. e. they do not respond to pain themselves, but respond to spastic contractions of other muscles;
- A pre-generated feeling of discomfort—it may be of varying intensity and manifest long before it gets worse. Unpleasant feelings can plague patients for days or even weeks before more serious signs of osteochondrosis appear. Usually, the discomfort is limited to the back and breastbone and may go away or worsen again;
- In osteochondrosis, pathological symptoms are usually more pronounced at night. By morning, the patient is satisfied, although the osteochondrosis reappears during the cold season or during sudden exercise.
atypical symptoms
Osteopathy is insidious because its symptoms may not resemble back pain at all. Sometimes patients don’t even suspect that the problem with the disease is precisely the spine—they drink painkillers or heart medications that have absolutely nothing to do with the cause of the pain.
Have multiple symptoms and need to contact the clinic for professional advice from a doctor - osteochondrosis or heart disease can only be detected after a thorough examination
In order to suspect osteochondrosis, you need to know which manifestations may indicate the disease:
- The occurrence of pain in the heart area is more similar to the symptoms of angina pectoris or even myocardial infarction. This colic can last for several weeks, and the drugs used to dilate coronary blood vessels have no positive effect at all in this condition;
- Worsening of the disease can cause breast pain and a stretched feeling in women, just like during pregnancy. Therefore, when this feeling occurs, it is necessary to consult a breast doctor;
- Spasmodic pain in the upper abdomen, which some patients think is a symptom of gastritis, cholecystitis, or pancreatitis. Pain usually worsens with increased physical activity. Signs of this pathology can seriously affect the function of the gastrointestinal tract;
- bladder and reproductive organ function problems;
- Throat and esophagus pain, foreign body sensation and pain when swallowing.
Dorsago syndrome manifests with thoracic osteochondrosis, which is characterized by very severe sternum pain when getting up from certain positions (sitting or lying down). The unpleasant sensation behind the sternum is so intense that the patient has difficulty breathing, stiff muscles, pain when turning the neck, and lower back.
Back pain develops slowly. In the initial stage, discomfort occurs only during active exercise and persists over time. At the height of the disease, even deep breathing can cause painful back pain.
signs of heart pain
Patients often conflate heart pain with manifestations of osteochondrosis, which is not surprising, because with spinal disease, the discomfort in the sternum is so intense that patients fear the worst - heart problems. To differentiate between heart pain and osteochondrosis, you need to know the main features of heart pain:
- Localization - The correct definition of localization will make it possible to partially dispel doubts about rickets. Cardiac pain is mainly evident behind the breastbone or on the left half of the breastbone. It radiates between the shoulder blades and can give the jaw, feel in the left hand;
- Characteristics of Pain - Cardiac pain is characterized by an enviable persistence, it is oppressive, it is oppressive in nature, it bakes behind the breastbone, due to the sharpness with which it occurs, this pain is called"dagger";
- Predisposing factors - Often cardiac pain has a definite factor under which the pressure increases and discomfort occurs. It can be both physical activity and a factor in emotional distress, stress. At rest, when a person is relaxed and not tense, pain in the area of the heart usually does not occur, but angina can occur with even the smallest load that causes the narrowing of the blood vessels;
- Time Factor - Heartache doesn't last long, you can always be sure of its beginning and end. Usually, an attack of angina pectoris is embedded within a few minutes. The heart does not stab in advance, nor does it hurt or pull. In general, osteochondrosis can be distinguished from true cardiac pain, which is a period of previous discomfort, the duration of which is mainly limited to 15-20 minutes;
- The nature of chest pain cessation is also an important factor for physicians to consider when distinguishing between osteochondrosis and heart disease. Often, a heart attack occurs quickly, and the patient needs to stop the irritant - stop exercising or calm down when stress is present. You can take a nitroglycerin tablet, and in most cases, it will help relieve the discomfort and even stop the pain completely within a few minutes. With myocardial infarction, nitroglycerin cannot cope with the pain, and the patient needs emergency help.
Suggest!These features are typical of heart pain, however, angina can also cause shortness of breath, leading to stomach pain. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of the symptoms present must be carried out, taking into account the relationship and focusing on the cardiac manifestations.
The problem of diagnosing heart disease is not always solved by patients who at least do not understand how real heart pain manifests, and the discomfort of osteochondrosis, so doctors in critical situations advise not to delay the manifestation of the pathology, always call an ambulancehelp".
Osteochondrosis is the cause of heart pain
Soreness behind the breastbone can be a manifestation of pure osteochondrosis, real heart pain, but don't ignore the impact of osteochondrosis itself on the heart. Doctors have long talked about the disease's link to heart pain, but now scientific research has confirmed the mechanism by which heart pain occurs and its cause is a problem with the musculoskeletal system, known as osteochondrosis. chest area.
There are nerve connections between the spine and the heart, affecting the heart's work and causing organ dysfunction. The stellate ganglion plays an active role in the innervation of the heart, from which the vertebral nerves separate - part of the sympathetic plexus of the spinal artery.
The sympathetic plexus indirectly affects the brainstem and cortex. Thus, in osteochondrosis, neural connections trigger various cardiac pain syndromes, metabolic consequences affecting myocardial contractility, and the development of cardiac arrhythmias.

Few people know that these two diseases are already present by the age of 40-50 years, and late diagnosis can lead to co-symptoms, which can lead to errors.
The diagnostic difficulty is that patients with osteochondrosis develop the disease in their forties and fifties, and at this age the first heart disease has already begun. As a result, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis and coronary heart disease often leads to errors—it is difficult to determine the cause of pain. The reasons for this are as follows:
- Underdiagnosed causes of heart pain;
- Cardiologists have limited knowledge about whether the heart can be injured by osteochondrosis;
- Reassessment of ECG results, according to which the patient is almost immediately flagged for one diagnosis or the other;
- There were no X-rays, which showed clear signs of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
Furthermore, the nature of projected pains, their localization, and the patient's perception are not always considered during the diagnostic process. Therefore, these shortcomings in diagnosis lead to approximately 80% of osteochondrosis patients receiving the wrong diagnosis - coronary heart disease - at the initial examination. Even an ECG with a high peak T wave confirmed the diagnosis, but doctors preferred the first factor without knowing whether it was the heart or the osteochondrosis.
Heart pain with osteochondrosis can be determined to be neurodystrophic, not ischemic, only with additional tests and x-rays. It is she who influences the heartache, causes the characteristic manifestations, and therefore leads to the misdiagnosis. The study also noted that heart pain occurred most often in those patients who already had organ disease, particularly atherosclerotic changes in the blood vessels.
important!The main threat to diagnosing this pain is that the ratio of coronary to non-coronary components is responsible for the discomfort behind the sternum. This aspect, the effect of osteochondrosis on the heart, is extremely difficult to single out.
One study observed that a patient with coronary insufficiency, a serious vascular disease, did not experience a myocardial infarction within a week of a heart spasm, despite the very threatening ECG data. However, the severity favored the non-coronary component.
In this case, the main role of the physician is to correctly diagnose the disease, to assess the patient's health, especially indicators of the work of the heart, and to predict the possible threat to the patient's life, since there is a related origin - coronary and non-coronaryHeart disease - it's hard to pick out the proportions of each. According to statistics, 100% of patients who come to the clinic are diagnosed with a pre-infarct condition or myocardial infarction.
pain relief
After the cause is identified and a diagnosis is made, the doctor will prescribe treatment – a detailed treatment plan that will help the patient manage pain and prevent complications. Treatment includes medication, physical therapy methods, homeopathy. The main treatments are:
- Bed rest is recommended until the pain completely subsides;
- To relieve heartache, analgesics, antispasmodics, steroidal or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended when osteochondrosis is detected, but should not be abused because of their adverse effects on the gastrointestinal tract;
- In addition to oral medications, various anesthetic creams, gels, and oils can be used. Effective medicines with safe ingredients are those based on bee venom, turpentine, and tea tree oil;
- To activate blood circulation, nootropics, chondroprotectants, vasodilators and diuretics will be useful;
- An excellent effect on the patient's body will be the passage of the physiotherapy process. The prescribed method will help to cope with the manifestations of osteochondrosis and strengthen the body with pain in the heart;
- Spinal acupressure, which specifically targets damaged tissue, will help with back pain and muscle stiffness. All areas suffering from spasms are relaxed and soreness is eliminated. At the same time, acupressure helps to correct posture;
- In the subacute phase, physiotherapy exercises are allowed, aimed at strengthening the muscles projecting to the thoracic spine. You can visit the swimming pool and take part in special fitness training;
- A diet will help to get rid of soreness - the doctor will individually recommend products for the pathology of the musculoskeletal system, as well as nutrition to correct the core, enriching it with substances necessary for the normal functioning of the heart muscle. Traditionally, for all patients, attention needs to be paid to the use of fat, sweet, salty, and, if necessary, to reduce excess weight.
the most important
Thoracic vertebral osteochondrosis refers to a degenerative dystrophic lesion of cartilage tissue that causes a person to experience severe pain and discomfort. The disease occurs mainly in patients over the age of 40, and its appearance is affected by joint pathology, trauma, genetic factors, stress, metabolic disturbances, imperfect working conditions, and hormonal disturbances. Osteochondrosis itself can cause pain similar to heart pain and also indirectly affects the development of cardiac pathology.
To differentiate the pathology, a special diagnostic test is performed - neocaine blockade of the stellate node, which helps to find out the diagnosis of the patient and correctly assess his condition. In addition, it is worth considering the irradiation of pain, the effectiveness or ineffectiveness of cardiac medications, and the presence of ECG changes over time.
Treatment is prescribed based on the cause of the disease, which can be identified after a thorough examination. Cardiac medications are recommended for coronary heart disease, whereas osteochondrosis can be cured with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotective agents, and in some cases surgery.