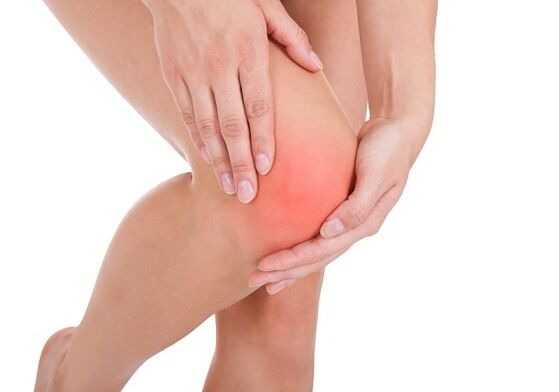
Knee pain is one of the most common unpleasant sensations, and everyone has experienced it at least once. As the disease progresses, pain may occur. This is because the human knee is composed of many structures and bears a huge load every day. The injury can affect one of the ligaments or tendons, or specific sacs filled with fluid, as well as cartilage. This symptom may be a signal not only of a disease related to the knee, but also a signal of a general disease of the body or system.
It is also necessary to distinguish what kind of exercise causes pain. For example, knee pain during flexion is inherent to people who live an active lifestyle. It is often said that it is the destruction of joints and bone structure. This type of spasm mainly occurs in the later stages of the disease course, and cannot be treated with surgical intervention at this time. The knee is often injured and tightened when squatting, which may indicate that cartilage tissue is being removed (mainly observed in athletes due to continuous running). Due to various pathologies of the joints or the occurrence of tumors, internal soreness appears. The appearance of postpartum pain is due to the many changes that women have undergone during pregnancy, which may lead to the occurrence of some diseases.
It is important to determine the cause of knee pain, because some diseases can only be cured by operable intervention, and for some diseases, the use of traditional medicine is sufficient.
Cause
As mentioned above, there are many causes of knee injuries, and they are not always directly related to knee injuries, diseases, and bruises. The first group of factors consists of diseases that directly affect the knee joint, including:
- Knee joint disease is a disease that most commonly affects people over forty years of age. Pathology usually affects both knees. The main symptoms are pain and crunching when stretching and squatting. The spasms are sharp. Decreased strength when lying down;
- Let blood enter the joint cavity;
- Meniscus injuries can occur at any age, regardless of gender. Usually only one knee is affected. This disease is characterized by strong tightness and pain in the knee after bending or running. In addition, a person loses the ability to move, because a slight movement of his leg will feel unbearable pain;
- Arthritis-This disease develops very quickly, and the inflammatory process spreads to the knee joints of the legs. It is best to start treatment as soon as possible because the disease has spread to other joints;
- Damage to the integrity of the ligaments due to rupture, the most common is that the internal ligaments are susceptible to this effect, and rarely occur on the lateral ligaments. In this case, there is swelling and motor function limitation;
- Various tendon inflammations-there are many causes, such as infection or bacterial influence, trauma or bruises, allergies to drugs, or abnormal body structure. In this disease, the knee joint is painful from the inside;
- Patella displacement or dislocation-rarely occurs after strenuous exercise or running, mainly in children or athletes;
- Inflammatory process in the joint capsule. If the treatment is not timely, complications may occur, which can only be eliminated with medical intervention;
- Pathological processes in the synovium covering the joints;
- Cysts on the inner side of the knee joint cause back pain under the knee;
- Destroy the integrity of the fatty tissue covering the joints. On the surface, this appears as swelling of the injured knee;
- Osteoarthritis, in which the cartilage tissue becomes thin;
- Various infectious diseases, the course of which can lead to arthritis. Knee pain when walking and after squatting;
- Bone tuberculosis;
- Spinal disease can cause knee pain when walking;
- Metabolic disorders or salt deposition in the knee joint often lead to knee joint pain when squatting.
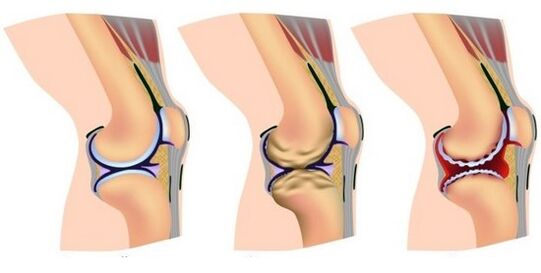
The second group of causes consists of other effects of knee pain:
- Excessive weight;
- Trauma or bruising of the knee joint;
- Working conditions in which a person is forced to stand for several hours;
- Vigorous physical activity-this is why this disease is most commonly observed in professional athletes, such as after running;
- Incorrect posture when working;
- Wearing uncomfortable high heels.
There are several reasons for women's knee injuries during pregnancy:
- Weight gain (up to 20 kg in some cases);
- Lack of calcium and other minerals in the body;
- Produce specific hormones that soften ligament tissue.
After childbirth, all unpleasant feelings will go away on their own, but if they do not happen, you should consult a doctor, as this may be a sign of the above-mentioned diseases. After childbirth, women may experience knee pain when squatting, standing, and stretching. This is due to the following reasons:
- High-intensity muscle exercise during childbirth;
- Involuntary sudden movements during the baby's birth can cause dislocation;
- If a woman suffers from various diseases of the musculoskeletal system before delivery;
- When breastfeeding a baby, a woman will accumulate fluid in her body, which can adversely affect the joints, so she feels pain when she gets up and stretches her knees.
symptom
In addition to the obvious signs-pain of different intensities and crunching when squatting, this manifestation also has other symptoms specific to the disease, causing knee injuries during walking or other leg movements:
- sleep disorder;
- Increased body temperature;
- Decreased appetite or total lack of appetite;
- Stiff movement
- Pain worsens when walking. Significant improvement in sitting or lying position;
- The injured knee is obviously swollen-it can be observed from the inside;
- Inability to shift the center of gravity to the sore limbs;
- Deformation of the patella;
- Changes in the skin color of the knees;
- fever.
When the first signs are shown, you must immediately contact a medical institution for diagnosis and an appointment for effective treatment.
diagnosis
Since many diseases can cause knee pain when walking, after running, squatting and standing, the diagnosis should include:
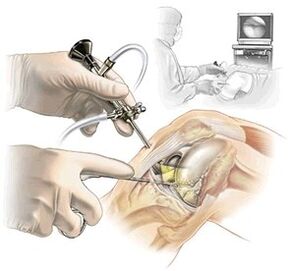
- A detailed investigation of the patient's initial symptoms, the intensity of the pain, the location (from the outside or the inside), and the possible cause (for example, while walking, after running, or after childbirth) that caused the pain;
- The attending physician palpates the knee joint to have a more comprehensive understanding of the location of pain and identify swelling;
- Analyze the patient’s blood for general and biochemical research;
- Radiography-any lesions of the knee joint structure will be clearly visible;
- Liquid sampling by puncture-if the attending physician suspects bone tuberculosis;
- Puncture fluid from the knee joint;
- Arthroscopy-performed when a meniscus injury causes pain on the inside of the knee. This method is not only used for diagnosis, but also for treatment;
- Measure bone tissue density;
- Knee joint ultrasound;
- Use MRI and CT to examine the patient.
treat
There is no single way to cure all diseases and obstacles. The treatment method for each patient is individually prescribed, depending on the cause and the severity of the spasm, if the knee is painful when walking, running, squatting or standing. The treatments prescribed for all patients without exception, including postpartum women:
- Reduce the load on the lower limbs to avoid the slightest symptoms;
- Apply a fixed bandage on the injured knee;
- Warm your knees with warm ointment or compresses. Use cold compresses as prescribed by your doctor, but no more than 15 minutes a day;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
If necessary, it can be treated with surgery.
In addition, there are alternative therapies that can reduce the onset of symptoms, but they can only be used after consulting a doctor. Such pain treatments include:
- Iodine tablets
- Compressed from your own urine;
- A mixture of raw potatoes and kerosene;
- Apple cider vinegar emulsion mixed with egg yolk;
- Ointment made from chopped potatoes with horseradish;
- Onion compress, for this you need to cut it in half, and then apply it on the outside and inside of the knee;
- Cologne and dandelion solution;
- A tincture of elecampane root and alcohol;
- Compresses of black elderberry, chamomile and muffins;
- Calendula lotion;
- A mixture of mustard and honey.
It is not recommended for women to use folk remedies during pregnancy and after delivery, when the baby is breastfeeding.
prevention
To avoid knee pain when walking, after running or squatting, you need to:
- Stick to a healthy lifestyle;
- Monitor your posture at all times;
- Keep your weight normal;
- Warm up the muscles before training to prevent knee joint cramps after running and exercise;
- Wear only comfortable shoes;
- Treat all diseases that may cause this disease in a timely manner;
- Receive routine check-ups in the clinic several times a year;
- If a person’s lifestyle or working conditions are in a standing or sitting position, gymnastics is performed;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Consult your doctor when symptoms first appear, especially after childbirth or running.