The symptoms of this disease depend on the stage. At the beginning, this was almost no discomfort when walking and exercising. It may appear in the form of mild pain in the hip area and disappear when resting. In this case, pain is felt not only in the thigh, but also in the groin or knee.
Cause of occurrence
Why does hip joint arthritis occur and what is it? The cause of hip joint disease may be different, but the condition of the disease is always the same. It all started with changes in articular cartilage, which became thinner and lost its ability to absorb loads. The human body compensates for the layering of cartilage tissue by forming bone growth along the edges of the joint surface, which causes different degrees of joint and bone deformation.
The main cause of this joint disease:
- Harm. Such causes may not be the main pathology, but in many cases, the development of the disease is affected by chronic microtrauma, which leads to the rupture and thinning of cartilage. They also affect the tearing of the joint capsule, leading to the accumulation of many injuries. Usually, repetitive microtrauma is a precursor to this disease.
- Excessive load, resulting in minor injuries to the system and joint injuries. The most common situation occurs in people engaged in physical labor or professional athletes. In this case, treatment without lifestyle changes or restricted movement is also ineffective, and relapses are often accompanied.
- genetic predisposition. These include abnormal development of the femoral head itself, dysplasia of joint elements and so on. In this case, so-called hip dysplastic arthritis occurs.
- Disease. For example, if not treated correctly, arthritis can develop into arthritis over time. This is due to the fact that during arthritis, the characteristics of cartilage tissue change and blood circulation is impaired. This gradually led to the development of the degradation process.
- Overweight. Overweight, even walking, will cause joints to bear loads that exceed their physiological strength limits.
According to the cause of the disease and its pathogenesis, there are two main types of arthritis in the hip joint.
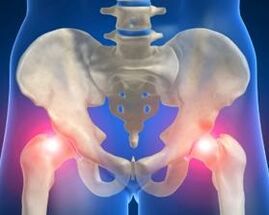
- Primary hip joint disease. In this case, the disease progresses very slowly and begins to invade the blood supply of the tissue. The cause of this type of arthritis is due to metabolic disorders, which are more common in people over 50. Primary arthritis of the hip is the most common diagnosis method.
- Secondary hip joint disease. In this case, the disease develops on the background of systemic inflammatory lesions in many joints in the body. Inflammation can be infectious in nature or autoimmune.
Symptoms of hip arthritis
The symptoms of hip joint hip joint disease should not be ignored and may lead to serious consequences. There are several main symptoms of the disease, depending on the stage of the disease:
- Pain in the joint area is the most obvious symptom and can be considered any hip disease. The intensity and nature of the sensations usually depend on the stage.
- Limitation of limb movement is also a symptom of hip arthritis. The early characteristic is the "stiffness" of the joints, which disappears after fatigue.
- Weakness of the thigh muscles can already be observed in the second stage of the disease, and complete atrophy in the third stage. Changes in leg length caused by pelvic deformities are characteristic of "advanced" osteoarthritis.
- La line or gait changes are likely signs of skeletal deformities.
- Significant joint contraction is not always a sign of joint disease. It is usually considered when other symptoms appear.
Hip arthritis 1 degree
This stage of the disease is characterized by joint and hip pain after exertion, sometimes in the knee, and sinking after rest. Unrestricted joint mobility, no gait disturbance.
2nd degree arthropathy of the hip
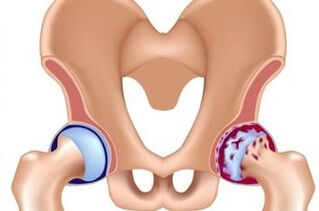
It is more clearly expressed-the intensity of pain increases, not only after exercise, but also during rest, exercise function is restricted. In particular, hip replacement is characterized by difficulty in internal rotation (inward rotation of the hip) and abduction, and contractures are formed.
X-ray examination showed a narrowing of the joint space and bone growth on the surface. Deformation of the acetabulum and femoral head. The thigh muscles begin to shrink on the affected side, and the pain syndrome spreads below, while capturing the knee joint and groin area (it is important to understand that this will not be accompanied by degenerative changes in the knee joint).
Grade 3 hip joint disease
The signs of this disease are obvious and permanent. Pain syndrome is prevalent at night. When walking, the patient needs support. The muscles of the calf and thigh gradually atrophy, and the affected leg becomes shorter and shorter.
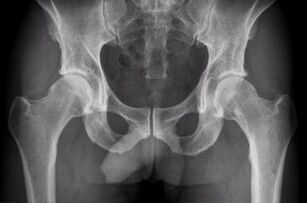
Usually, at the 3rd degree, the joint space completely disappears and the joints grow together into a single bone structure, which is demonstrated in the photos. As a result, complete immobility of the joints occurred.
Diagnosis
Before figuring out the treatment of hip arthritis, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis. If hip arthritis is suspected, a person will be referred for a biochemical blood test-if a certain disease is present, the patient's ESR, globulin, immunoglobulin and serum steroids will increase slightly.
The next step in detecting joint disease is X-ray pictures. It will display:
- Cartilage ossification
- Bone growth at the cartilage boundary
- Reduce the distance between joints,
- Thickening of subchondral bone tissue.
Unfortunately, X-ray photos do not allow to see the joint capsule and cartilage itself. If it is necessary to obtain information about these soft tissues, an X-ray scan will be performed on the patient.
Treatment of hip joint arthritis
When diagnosed with hip arthritis, treatment will directly depend on the stage of the disease. The general treatment plan can achieve the following goals:
- Eliminate pain and discomfort in joint sore areas;
- Adjust the nutrition of the cartilage in the joint and start its repair process;
- Eliminate the lack of fluid in the joint cavity;
- Activate the microcirculation in the joint tissue;
- Eliminates the increased load on the hip joint;
- Strengthen the muscles that surround, protect and support joints;
- can prevent deformities and increase hip joint mobility.
All these goals can only be achieved with a comprehensive approach, which should include not only medications, but also lifestyle changes to get rid of the risk factors of hip arthritis.
- In the third stage of the disease, treatment involves surgery. During this process, the joint will be replaced by an endoprosthesis, while part of the prosthesis is implanted in the femur and the other part in the pelvis. This operation is quite complicated, time-consuming and requires a long repair time.
- For hip arthritis of grade I and II, it can be treated without surgery. Second-hand products: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectants, vasodilators, hormone steroids, topical drugs-ointments, lotions, dressings.
All these medicines are prescribed by the attending doctor. Certain medications are effective by injecting directly into the affected joint area. Such injections can only be performed by qualified medical personnel. Therefore, self-medication is strictly not recommended.
Non-drug methods
In addition to using drugs, doctors also recommend non-drug methods to treat the disease. These include the following treatments for the disease:
- Physiotherapy;
- Massage;
- Joint breeding;
- Eating.
Physical therapy for arthritis includes the following treatments:
- Magnetic therapy;
- UHF and ultrasound therapy;
- Aviation and electrotherapy;
- Induction;
- Light therapy;
- Application of laser technology.
All these methods can only be used to improve the blood supply to the joints and relieve spasms.
Medications
Combined treatment of hip joint disease involves the appointment of the following types of drugs:

- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, all of them can relieve pain and inflammation, but they cannot restore cartilage tissue.
- Cartilage protector. Cartilage nutrition preparation. Speed up her recovery. It is very important in the 1. 2 stage of arthropathy treatment. In the third stage of the disease, cartilage has been destroyed, and these drugs will be useless. It takes a long time to take the medicine, and it takes several courses of treatment.
- Muscle relaxantsEliminate muscle spasms in the affected joint area and improve the blood supply to the tissues.
- Ointments and creams. Healing ointments are ways to alleviate the patient's condition, but they do not help complete recovery. The warm ointment works well. They stimulate skin receptors, thereby reducing pain. Heating ointment can also restore blood circulation in the tissues and muscles around the affected joint.
- Inject steroids into the joint cavity, these injections of drugs can reduce the deterioration of the disease and eliminate severe pain.
- VasodilatorExpand the blood vessels in and around the joint cavity, thereby improving the delivery of nutrients necessary for tissue repair.
No need to rely too much on folk remedies. However, some therapists recommend using lemon, garlic or celery root tincture to treat joints and bones.
Massage treatment of cervical spondylosis
In the case of hip joint deformation, massage therapy can achieve good results. Massage treatment of hip arthritis is a very effective and useful method. It is best to have a good expert perform the massage, and massage as much as possible.
Its role is to improve blood circulation, strengthen muscles, relieve painful cramps, swelling and muscle tension, and increase joint transfer between joints.
In the absence of a professional masseur, you can massage yourself. Joint massage can be performed manually, or with the help of various massage equipment or even water flow (hydrodynamic therapy).
Gymnastics
The purpose of treating hip arthritis through physical exercise is to achieve two goals: increase leg mobility and prevent muscle atrophy. All standard compounds of hip exercise therapy also have a general strengthening effect and have a positive effect on the whole body.
The complexity of gymnastics exercise is regulated by experts. The first few physical treatments should be performed under the guidance of a doctor. He will show you how to perform each movement correctly and monitor the proper load on the hip joint.
Diet
Key suggestions:
- Drink water porridge first.
- Eat enough animal protein: fish (except salted), poultry, beef.
- Eat at least five servings of vegetables every day (one serving is 100 grams and can be used as a side dish).
- Need dairy products: cheese, yogurt, fermented and baked milk.
- Eliminate alcohol, coffee and strong black tea.
- Eliminate sweet starchy foods.
- Eat smaller meals more often.
Diet will reduce the pressure on the hip joints and provide them with everything they need for tissue repair.